The routes of Christopher Columbus are a fascinating subject that intertwines exploration, adventure, and the eventual reshaping of the world as we know it. Columbus, an Italian navigator, embarked on a series of voyages that led to the European awareness of the American continents, changing the course of history forever. This article delves into the specifics of Columbus's routes, the significance of his discoveries, and their lasting impact on global history.
In this comprehensive exploration, we will examine the different voyages undertaken by Columbus, the motivations behind these journeys, and the historical context of his expeditions. By understanding Columbus's routes, we gain insight into the Age of Exploration, a period that marked significant changes in trade, culture, and geopolitics.
Join us as we embark on an informative journey through the significant routes of Christopher Columbus, analyzing the impact of his discoveries on the world and the legacy that remains today. This exploration will not only highlight the details of his voyages but also emphasize the importance of understanding our past.
Table of Contents
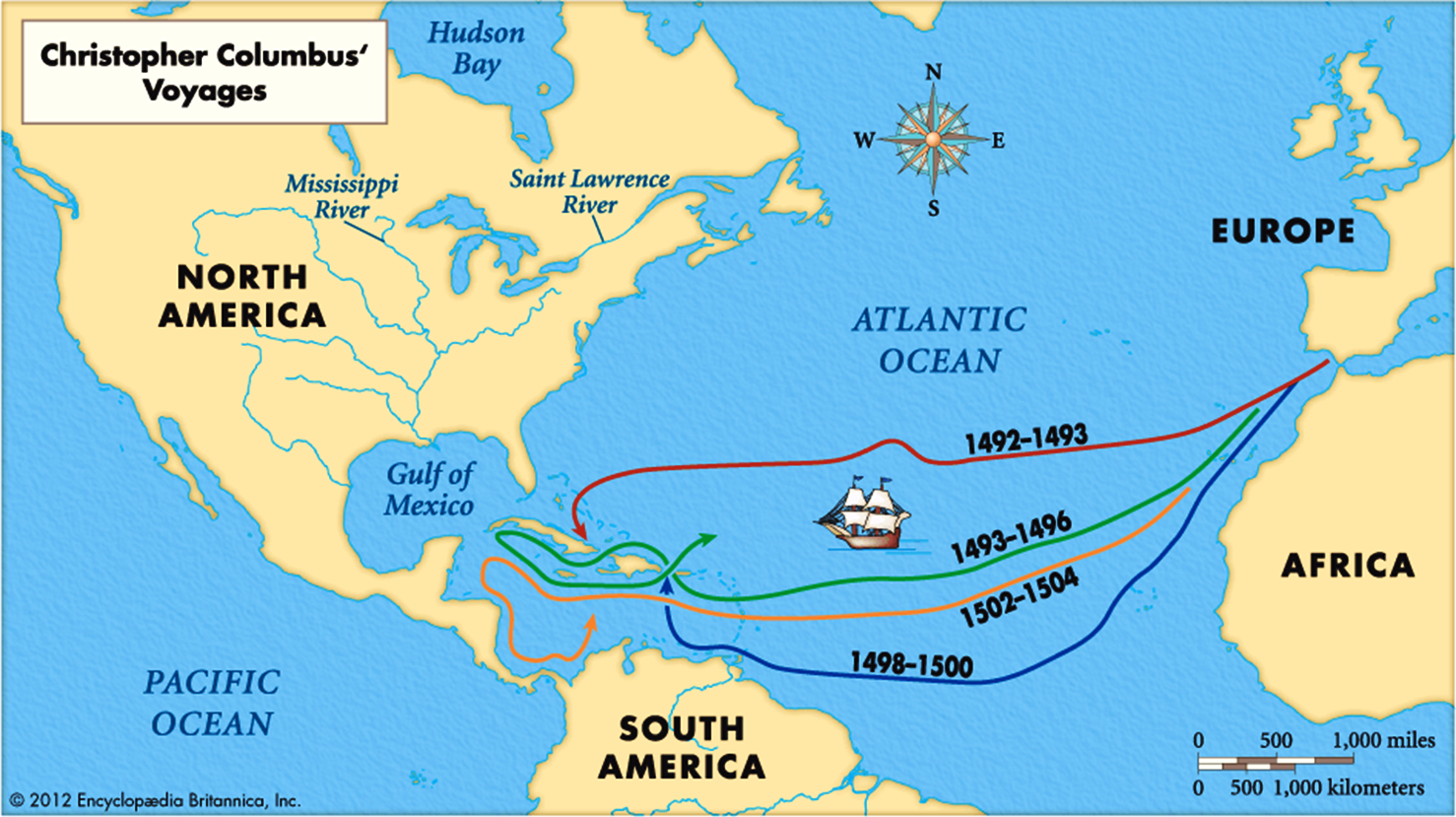
- The First Voyage: 1492-1493
- The Second Voyage: 1493-1496
- The Third Voyage: 1498-1500
- The Fourth Voyage: 1502-1504
- Motivations Behind the Voyages
- Impact of Columbus's Discoveries
- Criticism and Controversies
- The Legacy of Christopher Columbus
The First Voyage: 1492-1493
Christopher Columbus's first voyage set sail on August 3, 1492, with three ships: the Niña, the Pinta, and the Santa María. His aim was to find a westward route to Asia, motivated by the lucrative spice trade.
Columbus and his crew crossed the Atlantic Ocean, making landfall on October 12, 1492, on an island in the Bahamas, which he named San Salvador. This voyage marked the beginning of European exploration in the Americas. Other notable stops included Cuba and Hispaniola. Columbus returned to Spain in March 1493, bringing with him gold, spices, and the first indigenous people he encountered.
The Second Voyage: 1493-1496
Columbus's second voyage commenced on September 24, 1493, with a much larger fleet of 17 ships. His objectives expanded to establishing a permanent settlement in the New World.
This journey led Columbus to the Lesser Antilles and back to Hispaniola, where he found the settlement he had previously established in disarray. He worked on fortifying his position, hoping to convert the indigenous population to Christianity and exploit the land's resources.
The Third Voyage: 1498-1500
On May 30, 1498, Columbus embarked on his third voyage, this time reaching the South American mainland. He explored the coasts of present-day Venezuela and Trinidad.
Columbus faced increasing challenges during this voyage, including resistance from indigenous peoples and dissatisfaction among his crew. His attempts to find a strait to the Indian Ocean were unsuccessful, leading to heightened tensions and conflicts.
The Fourth Voyage: 1502-1504
The final voyage, which began on May 11, 1502, aimed to find a passage to the Indian Ocean. Columbus explored parts of Central America, including Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica.
Despite facing numerous hardships, including shipwrecks and hostile encounters, Columbus's fourth voyage contributed to the understanding of the geography of the New World.
Motivations Behind the Voyages
Columbus's motivations were multifaceted, including:
- Economic: Seeking new trade routes to access spices and precious metals.
- Religious: Aiming to spread Christianity among indigenous populations.
- Personal: Aspiring for fame, fortune, and titles from the Spanish crown.
Impact of Columbus's Discoveries
The impact of Columbus's voyages was profound and far-reaching:
- Initiation of the Columbian Exchange, which transformed agriculture and diets globally.
- Opening new trade routes that connected Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
- Colonization and significant changes to indigenous societies and cultures.
Criticism and Controversies
Columbus's legacy is not without controversy. Critics argue that his expeditions led to the exploitation and suffering of indigenous peoples, raising ethical concerns about his actions. The consequences of colonization included disease, slavery, and the destruction of native cultures.
The Legacy of Christopher Columbus
Despite the controversies, Columbus's voyages are recognized as pivotal moments in history. His expeditions marked the beginning of sustained European contact with the Americas, forever altering the course of history. Today, Columbus is both celebrated and critiqued, reflecting the complex legacy of his journeys.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the routes of Christopher Columbus represent a significant chapter in the narrative of human exploration and interaction. His voyages opened up new horizons and initiated profound changes that shaped the world. As we reflect on his journeys, it's essential to consider both the achievements and the consequences of his actions.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts on Columbus's legacy and its implications for our understanding of history. Please leave a comment or share this article with others interested in the Age of Exploration.
Final Thoughts
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of Christopher Columbus's routes. We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into his journeys and their significance. We invite you to explore more articles on our site for a deeper understanding of historical events and figures.