The invention of the motor car revolutionized transportation, shaping modern society and economies around the globe. Understanding who invented the motor car involves delving into the history of automotive engineering, the key figures involved, and the technological advancements that led to the creation of the first practical automobile. This article seeks to provide a comprehensive overview of this pivotal moment in history, examining not just the inventor but also the context and implications of this groundbreaking innovation.
From the earliest steam-powered vehicles to the gasoline-powered cars we know today, the development of motor cars is a fascinating journey. In this article, we will explore the contributions of various inventors, highlight significant milestones in automotive history, and discuss the impact of these innovations on our daily lives. We will also address common misconceptions and provide insights into how the motor car has evolved over the years.
As we embark on this exploration of who invented the motor car, we aim to provide in-depth knowledge and insights into this pivotal invention. Whether you're a car enthusiast, a history buff, or simply curious about the origins of motor vehicles, this article is tailored to inform and engage you.
Table of Contents
- Biography of the Motor Car Inventor
- Key Milestones in Automotive History
- Early Inventions Leading to the Motor Car
- The First Practical Automobile
- Impact of the Motor Car on Society
- Modern Advancements in Automotive Technology
- Common Misconceptions about Motor Car Invention
- Conclusion
Biography of the Motor Car Inventor
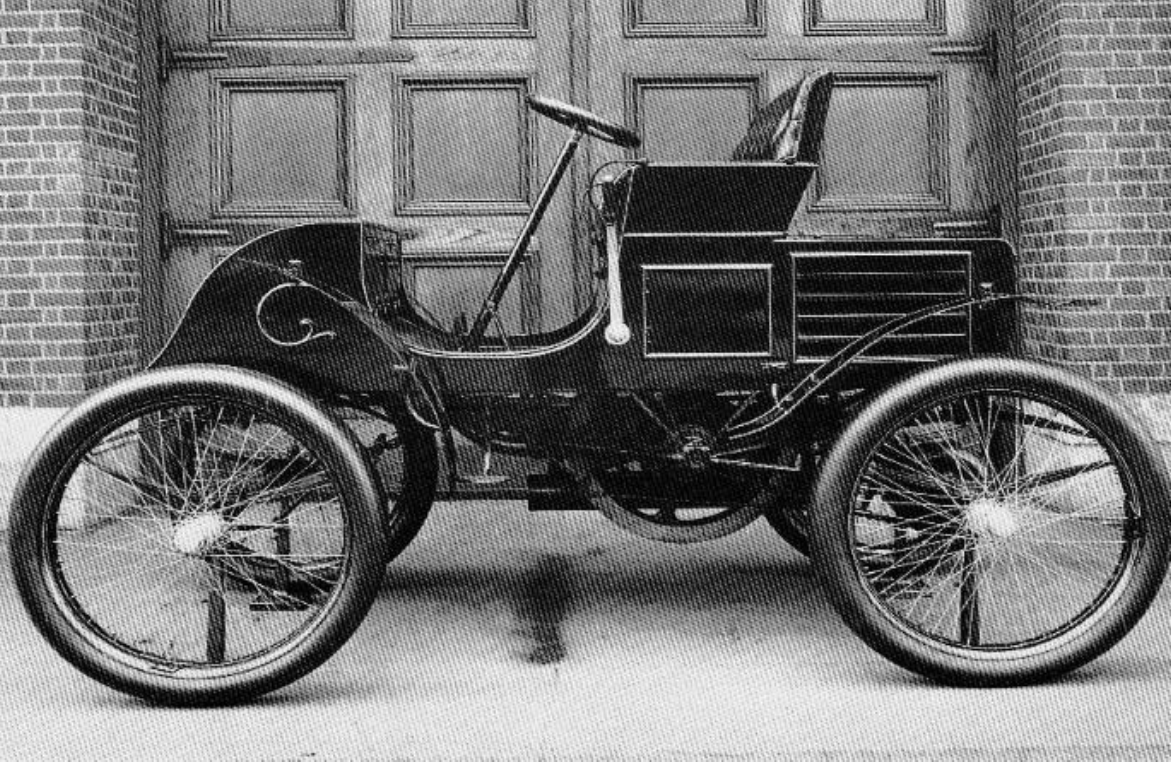
The invention of the motor car cannot be attributed to a single individual; however, Karl Benz is widely recognized for creating the first practical automobile. Born on November 25, 1844, in Karlsruhe, Germany, Benz was an engineer who played a crucial role in the development of the internal combustion engine.
| Name | Karl Benz |
|---|---|
| Date of Birth | November 25, 1844 |
| Nationality | German |
| Notable Invention | Benz Patent Motorwagen (1886) |
| Date of Death | April 4, 1929 |
Early Life and Education
Karl Benz showed an early interest in engineering, enrolling in the Polytechnic School in Karlsruhe at the age of 15. After graduating, he worked in various engineering firms, gaining valuable experience that would later contribute to his groundbreaking work in automotive design.
Invention of the Motor Car
Benz’s most significant achievement came in 1886 with the invention of the Benz Patent Motorwagen, which is considered the first true automobile. This three-wheeled vehicle was powered by an internal combustion engine and was a significant step forward in automotive technology.
Key Milestones in Automotive History
The journey to the modern motor car is marked by several key milestones that reflect the evolution of automotive technology.
- 1769: Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot built the first full-scale, working steam-powered vehicle.
- 1885: Gottlieb Daimler invented a high-speed gas engine.
- 1886: Karl Benz patented the first gasoline-powered automobile.
- 1908: The Ford Model T was introduced, making cars more accessible to the masses.
- 1930s: The introduction of automatic transmissions and safety features.
- 21st Century: Advancements in electric vehicles and autonomous driving technology.
Early Inventions Leading to the Motor Car
Before the motor car, several inventions paved the way for its development. These include:
The Steam Engine
The steam engine was one of the first technologies that allowed for the development of mechanized vehicles. Inventors like James Watt significantly advanced steam technology in the late 18th century, laying the groundwork for future innovations.
Gasoline Engines
The transition from steam to gasoline engines marked a crucial turning point in automotive history. The development of the internal combustion engine by inventors like Nikolaus Otto and Gottlieb Daimler played a pivotal role in making motor cars practical and efficient.
The First Practical Automobile
The Benz Patent Motorwagen, completed in 1886, is widely regarded as the first practical automobile. It featured several innovative designs:
- Internal combustion engine
- Electric ignition system
- Water-cooled engine
- Flexible leather belt for the drive
In 1888, Benz's wife, Bertha, undertook a long-distance journey in the Motorwagen, which served as a publicity stunt and demonstrated the vehicle's practicality. This journey is often considered the first road trip in automotive history.
Impact of the Motor Car on Society
The invention of the motor car had profound effects on society, including:
Economic Growth
Automobiles spurred economic growth by creating jobs in manufacturing, sales, and maintenance. The automotive industry has become one of the largest sectors in many economies worldwide.
Urban Development
The rise of motor vehicles led to significant changes in urban planning and development, including the expansion of road networks and suburban areas.
Modern Advancements in Automotive Technology
Today, the automotive industry continues to evolve with advancements such as:
- Electric vehicles (EVs)
- Autonomous driving technology
- Advanced safety features (e.g., automatic braking, lane-keeping assistance)
- Connected car technology (e.g., Internet of Things integration)
Common Misconceptions about Motor Car Invention
Many people believe that the invention of the motor car is solely attributed to Karl Benz; however, it is essential to recognize the contributions of other inventors and the collective advancements in technology that led to the creation of the automobile.
The Role of Other Inventors
Figures like Gottlieb Daimler and Henry Ford played critical roles in the development and popularization of automobiles, each contributing unique innovations that shaped the industry.
Myth of the First Car
Another common misconception is that the Benz Patent Motorwagen was the first car ever made. In reality, several other prototypes and designs existed, but Benz's creation was the first to be commercially viable and recognized as an automobile.
Conclusion
In summary, the invention of the motor car was a monumental achievement that involved numerous inventors and technological advancements. Karl Benz's creation of the Benz Patent Motorwagen in 1886 marked a turning point in transportation, leading to significant societal changes and economic growth. As we continue to embrace new technologies in the automotive industry, it is crucial to appreciate the rich history that brought us to this point.
We encourage you to share your thoughts in the comments below, and feel free to explore other articles on our site to learn more about the fascinating world of automotive history and innovation.
Final Thoughts
Thank you for taking the time to explore the history of the motor car with us. We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights and knowledge. We look forward to welcoming you back for more engaging content in the future!